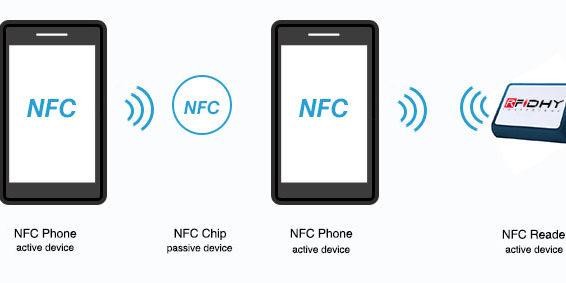
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a short-range wireless communication standard similar to BLE or Wi-Fi, but works over short range typically 10cm or less. NFC is a radio frequency (RF) signal initiated by an active NFC device such as a smartphone or reader, and another active or passive device such as an NFC tag to transfer data.
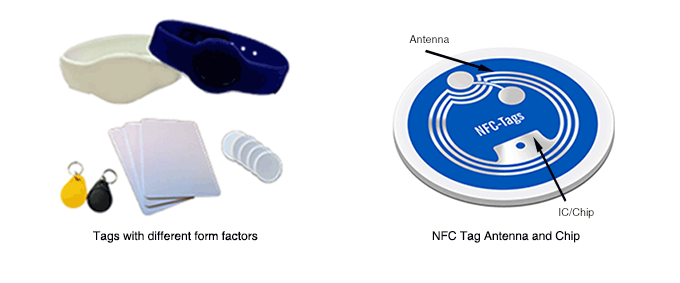
All NFC tags consist of an antenna coil and a small chip that is bonded to the antenna. When a mobile phone is within range of an NFC tag, its antenna becomes energized and powers the chip, which stores data. This antenna plus chip combo can be embedded inside a variety of form factors: circular/square stickers, business cards, access control cards, keychains, bank cards and even e-passports. Typically, the larger the antenna the longer the read range. The chip memory size ranges from 144 bytes, large enough to store a URL, to 36 kilobytes to store a person’s photo on an e-passport.
WHICH PHONES HAVE NFC?
Most of the new Android, Windows and Blackberry smartphones come with NFC as a built-in feature. NFC World keeps a comprehensive and up-to-date list of the available smart devices available in the market. To start using NFC on your phone, insure that NFC is enabled on your device. To scan a tag bring the device a few centimeters away from the tag. Apple has included NFC in the iPhone 6, but for now it can only be used for Apple Pay.
If you are integrator, please contact us directly; If you are looking for an entire solution, we can introduce you your local integrator to help you out.